Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
3 Optics Valley Laboratory, Hubei 430074, China
Interaction of intense laser fields with atoms distorts the bound-state electron cloud. Tracing the temporal response of the electron cloud to the laser field is of fundamental importance for understanding the ultrafast dynamics of various nonlinear phenomena of matter, but it is particularly challenging. Here, we show that the ultrafast response of the atomic electron cloud to the intense high-frequency laser pulses can be probed with the attosecond time-resolved photoelectron holography. In this method, an infrared laser pulse is employed to trigger tunneling ionization of the deforming atom. The shape of the deforming electron cloud is encoded in the hologram of the photoelectron momentum distribution. As a demonstration, by solving the time-dependent Schrödinger equation, we show that the adiabatic deforming of the bound-state electron cloud, as well as the nonadiabatic transition among the distorted states, is successfully tracked with attosecond resolution. Our work films the formation process of the metastable Kramers-Henneberger states in the intense high-frequency laser pulses. This establishes a novel approach for time-resolved imaging of the ultrafast bound-state electron processes in intense laser fields.
Ultrafast Science
2022, 2(1): 9842716
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan 430205, China
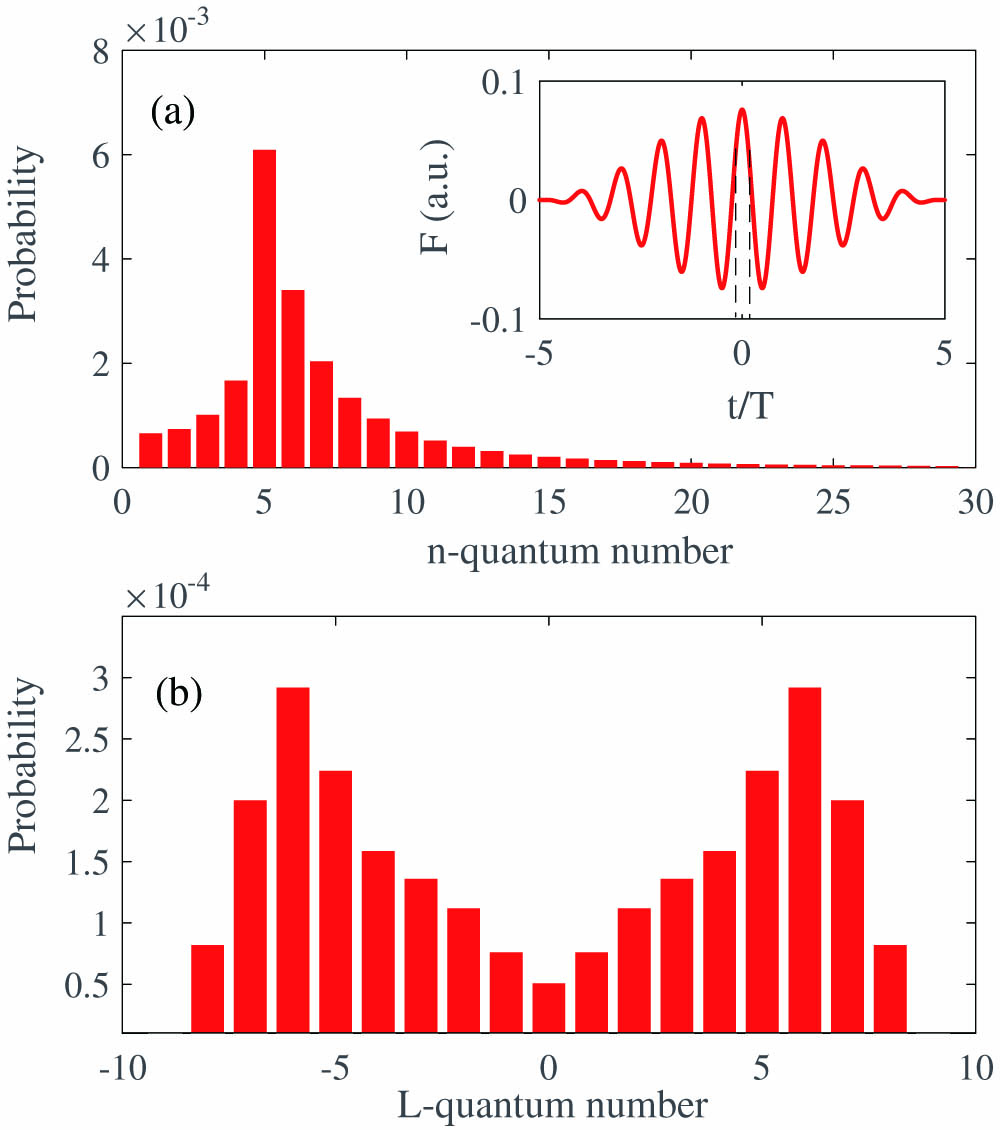
Using the classical-trajectory Monte Carlo model, we have theoretically studied the angular momentum distribution of frustrated tunneling ionization (FTI) of atoms in strong laser fields. Our results show that the angular momentum distribution of the FTI events exhibits a double-hump structure. With this classical model, we back traced the tunneling coordinates, i.e., the tunneling time and initial transverse momentum at tunneling ionization. It is shown that for the events tunneling ionized at the rising edge of the electric field, the final angular momentum exhibits a strong dependence on the initial transverse momentum at tunneling. While for the events ionized at the falling edge, there is a relatively harder recollision between the returning electron and the parent ion, leading to the angular momentum losing the correlation with the initial transverse momentum. Our study suggests that the angular momentum of the FTI events could be manipulated by controlling the initial coordinates of the tunneling ionization.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 020.4180 Multiphoton processes 320.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 040202





